upm, memory deduplication for serverless
User-Guided Page Merging (UPM) Single-source model for productive serverless programming in C++
In serverless, applications use short-lived and stateless functionsexecutedexecuted in isolated containers or microVMs, which can quickly scale to thousands of instances and process terabytes of data. This flexibility comes at the cost of duplicated runtimes, libraries, and user data spread across many function instances, and cloud providers do not utilize this redundancy. The memory footprint of serverless forces removing idle containers to make space for new ones, which decreases performance through more cold starts and fewer data caching opportunities.
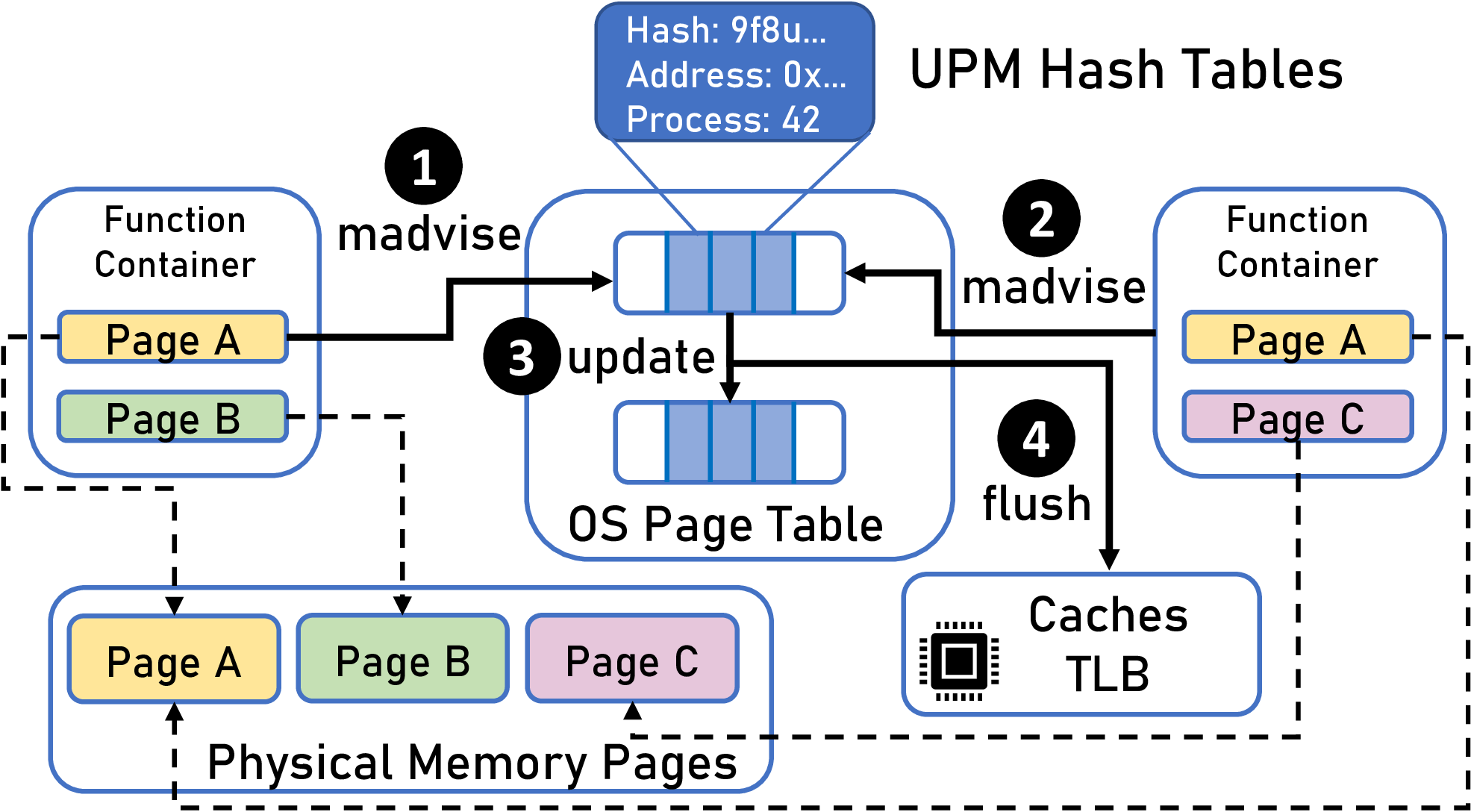
We address this issue by proposing deduplicating memory pages of serverless workers with identical content, based on the content-based page-sharing concept of Linux Kernel Same-page Merging (KSM). We replace the background memory scanning process of KSM, as it is too slow to locate sharing candidates in short-lived functions. Instead, we design User-Guided Page Merging (UPM), a built-in Linux kernel module that leverages the madvise system call: we enable users to advise the kernel of memory areas that can be shared with others. We show that UPM reduces memory consumption by up to 55% on 16 concurrent containers executing a typical image recognition function, more than doubling the density for containers of the same function that can run on a system.
More insights and results can be found in the paper. The kernel implementation is available on open-source license.